Enantioselective effect of trifloxystrobin in early-stage zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos: Cardiac abnormalities impacted by E,E-trifloxystrobin enantiomer
Abstract
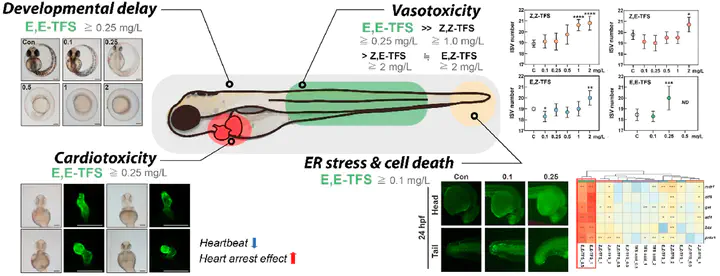
Trifloxystrobin (TFS) is one of the extensively used strobilurin fungicides, which is composed of four enantiomers and its active form is E,E-TFS. In this study, we assess the acute toxicity of four enantiomers, E,E−, E,Z-, Z,E−, and Z,Z-TFS in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Among the four enantiomers, only E,E-TFS was found to be acutely toxic, with an estimated LC50 value of 0.68 mg/L. Treatment with E,E-TFS resulted in various phenotypic changes in the embryos, including pericardial and yolk-sac edema, spine curvature, and blood pooling. And it shortened the whole body length in the treated embryos by increasing the total intersegmental vessel numbers using a Tg(fli1a:EGFP) zebrafish line. Further study using Tg(cmlc2:EGFP) zebrafish line revealed that E,E-TFS treatment was associated with cardiac malformations, a failure of heart function, and a lowered heartbeat rate at the concentration of 0.25 mg/L. Also, the differential gene expression analysis identified significant down-regulation of vmhc and cacna1c genes encoding ventricular myosin heavy chain and calcium voltage-gated channel subunit alpha 1C, which are crucial for heart development. These results suggest the need for regular monitoring of E,E-TFS enantiomers after field application and further research into their potential chronic effects on environmental organisms.