Effective phytosanitary treatment for export of Oriental melons (Cucumis melo var L.) using ethyl formate and modified atmosphere packaging to control Trialeurodes vaporariorum (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae)
Abstract
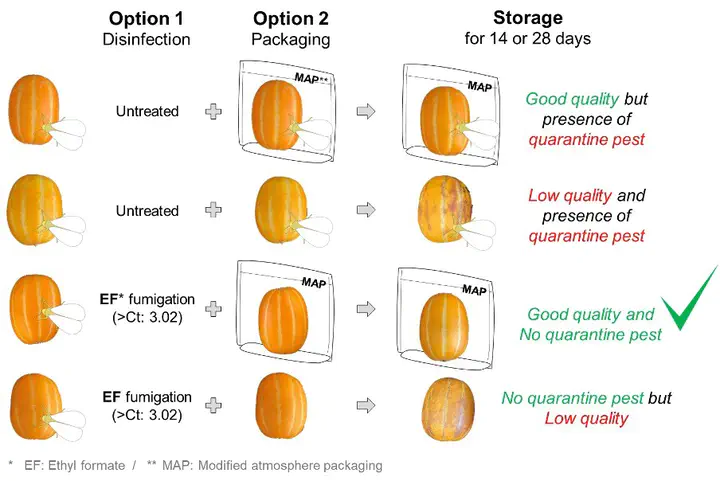
Trialeurodes vaporariorum (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae), commonly known as greenhouse whitefly, is one of the main insect pests of Oriental melon (Cucumis melo var L.) in South Korea. T. vaporariorum is of concern as a quarantine pest for the exportation of C. melo in Southeast Asian countries. Due to future restrictions on the use of methyl bromide (MB) during quarantine, ethyl formate (EF) represents a potential alternative. In this study, we evaluated EF for its efficacy (probit-9 values) in enabling the export of Oriental melons. The probit-9 value of EF for controlling T. vaporariorum was 3.02 g·h/m3 after 2 h of fumigation. We also assessed the phytotoxicity of EF on melons when using modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) under low-temperature conditions, which is required for export and trade, to extend shelf-life. In scaled-up trials, we found that 8 g/m3 EF for 2 h at 5°C to be suitable as a new phytosanitary treatment against greenhouse whitefly for exported Oriental melons when using MAP. No phytotoxic damage was found 28 d after fumigation at 5°C in terms of five quality parameters (firmness, sugar content, mass loss, color change, and external damage).